HAIR TRANSPLANT IN DELHI
What Is a Hair Transplant?
Many of us don’t think about our hair until it starts thinning or disappearing. For those facing hair loss, a hair transplant can restore the appearance of a fuller head of hair. This surgical procedure involves relocating your existing hair to areas of the scalp that are balding or thinning.
Hair transplant surgery has been practiced since the 1950s, but today’s techniques offer more natural and lasting results.
Hairline Transplants
A hairline transplant is specifically aimed at restoring a receding hairline. This condition is often associated with male pattern baldness, which primarily affects individuals assigned male at birth (AMAB). Hair loss typically starts at the temples and forehead, causing the hairline to recede.
Are Hair Transplants Permanent?
In most cases, hair transplants are designed to be permanent. Once the transplant heals, you can treat your new hair just like your natural hair—shampoo, comb, and style it as you like. However, some transplanted grafts may not survive, and a few could eventually fall out.
Types of Hair Transplant Surgery
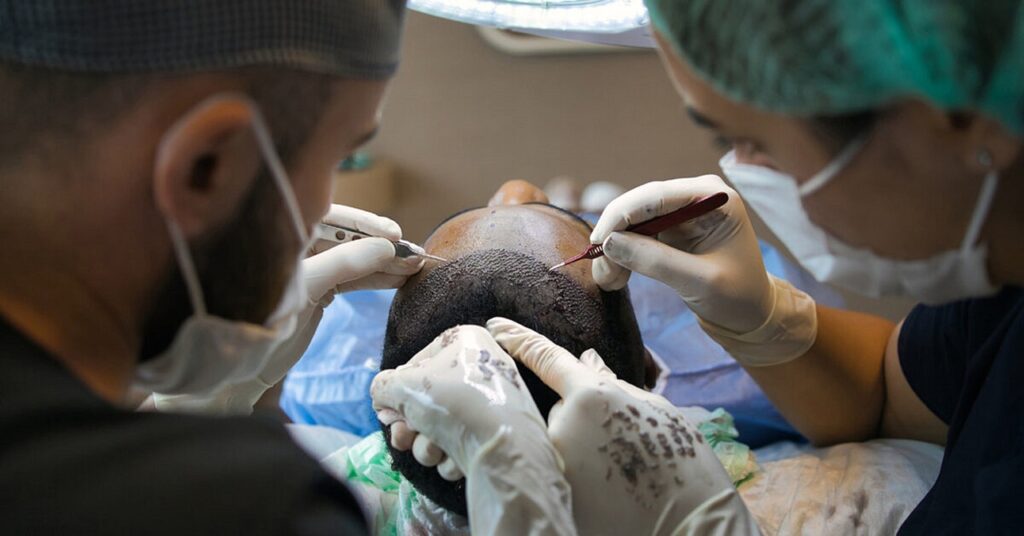
There are two primary types of hair transplant procedures: Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Both methods are performed in a clinical setting under local anesthesia.
Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS)
In FUSS, the surgeon removes a strip of skin, usually 6 to 10 inches long, from the back of the scalp. After stitching the wound, the strip is divided into smaller grafts, each containing individual hair follicles or small clusters. Depending on your needs, the surgeon may prepare between 500 to 2,000 grafts.
In an FUE procedure, the surgeon shaves the back of your scalp and individually extracts hair follicles. These follicles are then transplanted into balding areas. FUE leaves small dot scars that blend with the remaining hair.
FUSS vs. FUE: Pros and Cons
Each technique has its own advantages:
- Scarring: FUSS leaves a linear scar, while FUE results in less visible, dot-like scars.
- Time: FUSS is usually quicker, whereas FUE is more time-intensive due to the precision required.
- Appearance: FUSS doesn’t require shaving the back of the head, unlike FUE.
- Risk: FUE carries a slight risk of follicle damage during extraction, affecting transplant success.
- Cost: FUE is generally more expensive than FUSS.
Artificial Hair Transplants
Artificial hair transplants use synthetic fibers instead of natural hair. Though banned in the U.S. due to safety concerns, these procedures are still available in some countries. Artificial fibers may cause adverse reactions, so they are not as widely recommended.
How Does a Hair Transplant Work?
Hair transplants involve two main steps: harvesting and implantation.
- Harvesting: FUSS involves removing a strip of skin, while FUE extracts individual follicles.
- Implantation: The surgeon makes tiny incisions in balding areas to implant the hair grafts. This process may take several hours, depending on the number of grafts.
Who Is a Suitable Candidate?
Ideal candidates for hair transplants are those with androgenetic alopecia, a common form of hair loss that causes receding hairlines and thinning at the crown. Both AMAB and AFAB individuals with sufficient donor hair may qualify for this procedure.
Recovery and Growth Expectations
Post-surgery, you may experience tenderness, requiring pain relief and antibiotics. Bandages are worn for a couple of days. After 2-3 weeks, the transplanted hair sheds, but new growth typically appears within a few months. Most people see around 60% of new hair growth by the 6-9 month mark.
Hair Transplant Tips After Hair Treatment
Proper aftercare is essential to the success of a hair transplant. Following your doctor’s instructions will help ensure that your transplant heals and grows properly.
Avoid touching or scratching your scalp: Your scalp may feel itchy after surgery, but you should avoid scratching it. This can lead to graft dislocation and reduced yield.
Follow post-surgery instructions: Your surgeon will give you a comprehensive post-surgery hair care plan, including when to wash your hair and use prescription medications. Follow this plan carefully to get the best results.
Avoid direct sun exposure: Protect your scalp from direct sunlight for the first few weeks after surgery, as the sun can damage your skin.
Be gentle when washing your hair: Use a fragrance-free shampoo and blow-dry your hair gently. Avoid scrubbing too hard or using a hair dryer on high heat.
Monitor your skin for infections: although rare, infections can occur. Look for redness, swelling, or discharge, and talk to your doctor if unusual side effects occur.
Myths about hair types
When it comes to hair restoration, many people face misconceptions. Let’s define the most common business models:
1: Changing hair is dangerous
Usually, the equipment is “put down”. However, modern procedures such as FUE and FUS allow you to change your hair quickly and give it a natural look.
2: Only Men Can Change Their Hairstyle
While men experience hair loss more often, women are more likely to experience thinning or thinning hair, often due to hormonal changes, stress, or aging. Women who are designated as AFAB during pregnancy can undergo a hair transplant if they have enough hair to donate.
3: They Need to Take Care of Their Hair
If the sown grass is healthy, it’s natural. You don’t need any special shampoos or treatments; just use it to take care of your hair.
4: The Effects Are Instant
Although hair transplants can provide long-lasting results, it does take time. The transplanted hair usually falls out and new hair appears within a few months after the surgery. Patience is key, as it can take up to a year to see full results.
